Nucleotide Definition. A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of DNA and RNA. They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine, cytosine
Fact Sheet: DNA-RNA-Protein – microBEnet: the microbiology of the Built Environment network
3 days agoA nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T). In RNA, the base uracil (U) takes the place of thymine. DNA and RNA molecules are polymers made up of long chains

Source Image: scribd.com
Download Image
May 7, 2017 – You may need to name the three parts of a nucleotide and explain how they are connected or bonded. Here is the answer for both DNA and RNA.

Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
Dna Nucleotide Royalty-Free Images, Stock Photos & Pictures | Shutterstock
The three parts of a nucleotide are the base, the sugar, and the phosphate. Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA (2′-deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). DNA and RNA code genetic information, transport energy throughout cells, and serve as cell signaling molecules.
Source Image: microbiozindia.com
Download Image
What Are The Three Parts Of Dna Nucleotide
The three parts of a nucleotide are the base, the sugar, and the phosphate. Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA (2′-deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). DNA and RNA code genetic information, transport energy throughout cells, and serve as cell signaling molecules.
May 10, 2023Figure 2: The chemical assembly of the three parts of the nucleotide, the phosphate, the nitrogenous base, and the pentose sugar. This particular nucleotide is adenine The assembly of nucleotides has three key purposes. First, it differentiates them from nucleosides, which do not contain a phosphate group.
Significance of Nucleotides in Genome, Genetics and Molecular biology & Biochemistry
. Notice at collection . Mar 29, 2023 – Learn the three parts of nucleotide. Compare nucleotides in DNA versus RNA. Explore the structure of nucleotide subunits.
Which parts are the same in all nucleotides? – Quora
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
DNA Structure. Base Pairing and Nucleotide Stock Vector – Illustration of genome, medicine: 239446702
. Notice at collection . Mar 29, 2023 – Learn the three parts of nucleotide. Compare nucleotides in DNA versus RNA. Explore the structure of nucleotide subunits.

Source Image: dreamstime.com
Download Image
Fact Sheet: DNA-RNA-Protein – microBEnet: the microbiology of the Built Environment network
Nucleotide Definition. A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of DNA and RNA. They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine, cytosine
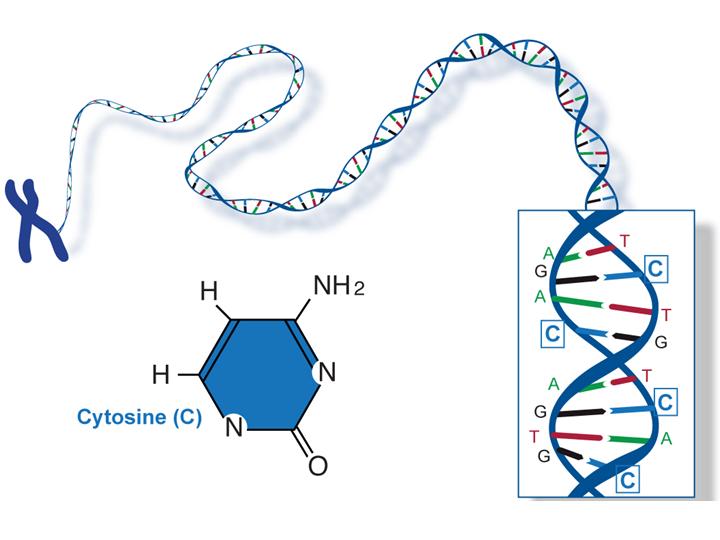
Source Image: microbe.net
Download Image
Dna Nucleotide Royalty-Free Images, Stock Photos & Pictures | Shutterstock
May 7, 2017 – You may need to name the three parts of a nucleotide and explain how they are connected or bonded. Here is the answer for both DNA and RNA.
Source Image: shutterstock.com
Download Image
What Are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide?
Each nucleotide monomer is built from three simple molecular parts: a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nucleobase. (Don’t confuse this use of “base” with the other one, which refers to a molecule that raises the pH of a solution; they’re two different things.) The sugar and acid in all four monomers are the same

Source Image: sciencenotes.org
Download Image
5,589 Nucleotide Images, Stock Photos, 3D objects, & Vectors | Shutterstock
The three parts of a nucleotide are the base, the sugar, and the phosphate. Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA (2′-deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). DNA and RNA code genetic information, transport energy throughout cells, and serve as cell signaling molecules.

Source Image: shutterstock.com
Download Image
Nucleotide – Definition, Structure (3 Parts), Examples & Function | Dna, Biologie, Chemie
May 10, 2023Figure 2: The chemical assembly of the three parts of the nucleotide, the phosphate, the nitrogenous base, and the pentose sugar. This particular nucleotide is adenine The assembly of nucleotides has three key purposes. First, it differentiates them from nucleosides, which do not contain a phosphate group.

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
DNA Structure. Base Pairing and Nucleotide Stock Vector – Illustration of genome, medicine: 239446702
Nucleotide – Definition, Structure (3 Parts), Examples & Function | Dna, Biologie, Chemie
3 days agoA nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T). In RNA, the base uracil (U) takes the place of thymine. DNA and RNA molecules are polymers made up of long chains
Dna Nucleotide Royalty-Free Images, Stock Photos & Pictures | Shutterstock 5,589 Nucleotide Images, Stock Photos, 3D objects, & Vectors | Shutterstock
Each nucleotide monomer is built from three simple molecular parts: a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nucleobase. (Don’t confuse this use of “base” with the other one, which refers to a molecule that raises the pH of a solution; they’re two different things.) The sugar and acid in all four monomers are the same